Today should be the last day of evidence in the Apple v. Samsung case. Closing arguments will likely be on Tuesday next week and then the jury will get the case. I posted earlier on the trade dress claims Apple has against Samsung that are in Apple’s complaint. In this post I’ll focus on Apple’s three asserted design patents related to the iPhone.
Design patents protect the appearance of an article rather than the functional features. Here is a table with the design patents and their titles:

When looking at a design patent, the solid lines show what is claimed and protected. Broken lines provide context but don’t limit the patent. So, while the D677 patent shows the iPhone 4, only the front screen area is in solid lines, so the side buttons and other features don’t restrict the scope of the patent. Similarly, the D790 patent claims the GUI. Only the icons and rectangular touch screen limit the scope of the patent. Below is a table comparing the Samsung Galaxy to these three patents:
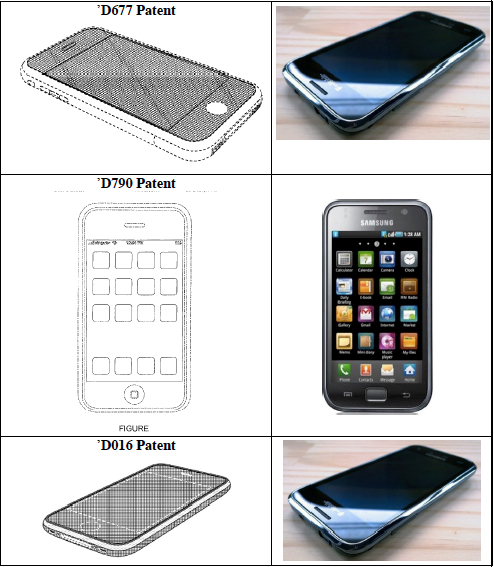
Samsung is attacking the validity of these design patents by trying to show that phones with the claimed design elements were publicly known prior to the filing of the applications that issued as these patents. Samsung can also avoid liability if they convince the jury that the design features are functional rather than aesthetic.
One thing Samsung won’t be able to rely on is an argument that they independently developed their own design. In copyright cases a defendant can avoid a claim of infringement if they came up with the material without any reference to the copyrighted material. That is because copyright law protects against, as the name suggests, copying. Patent law, however, doesn’t allow for a defense of independent development.
From what I’ve read so far, Samsung isn’t spending much time arguing that their designs are not similar to Apple’s, but are attacking the validity of the design patents. The jury will get to decide that issue.

